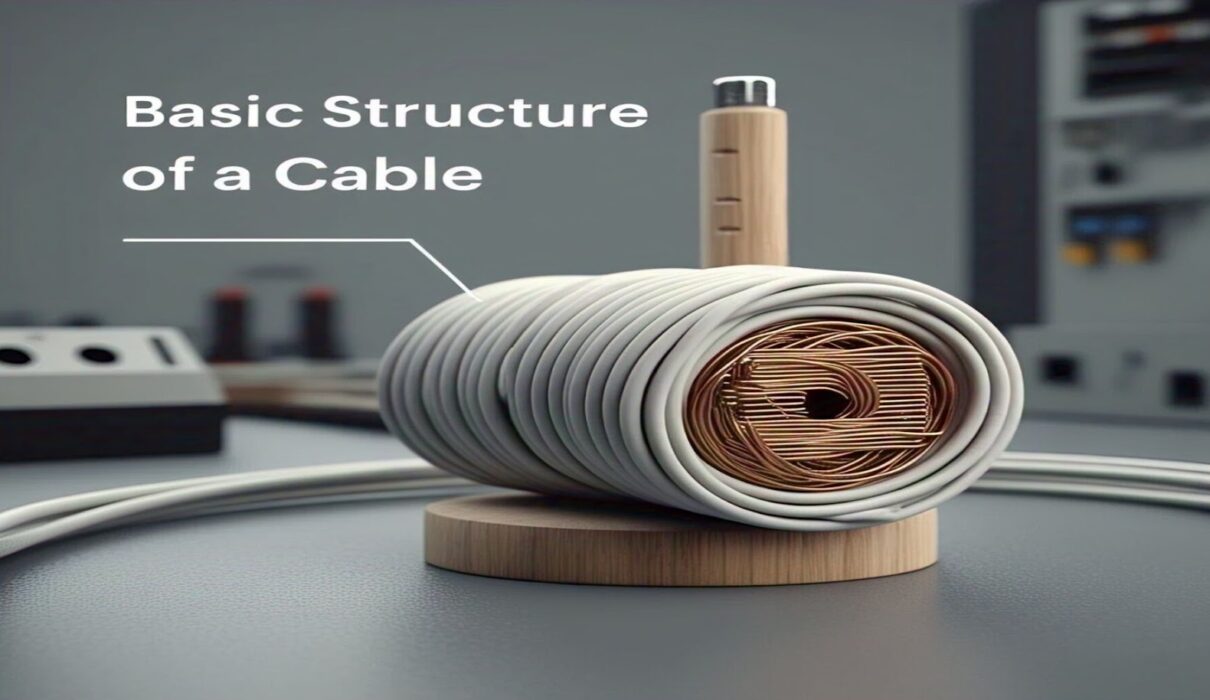
Basic Structure of a Cable
When you study the cable, it would include three main parts:
1. Inner conductors
It is an inner copper conductive metal wire that transfers electric current or data signals. Cables that use copper conductors are more powerful and are replaced by fibre optic cables. This is because the fibre optic cables use glass or plastic fibres for transmitting light signals at speeds so high that currently in advanced networks may reach up to 100 Gbps.
2. Cable Insulation
It is the Tradewind insulator that insulates cables from threats of electric shock and short circuits. PVC, rubber, and polyethene are the most common materials, but when you change the material it changes in heat and moisture resistance.
3. Shielding
This metallic or non-metallic layer acts as an additional shield to release EMI for reliable signal transmission. Proper shielding may improve up to 80% in signal quality by ensuring good environmental conditions at the transmitter and receiver’s side of the environment.
It is seen that the world’s longest undersea cable stretches to 19200 km from Asia, Africa, and Europe, and with it, brings high-speed internet into these three continents.
Areas of Application of Cables
Cables perform important functions in different industries, such as:
1. Power Transmission
Electricity is delivered through electrical cables from different power plants to homes, offices, and industries. It supports more than 99% of energy distribution worldwide.
2. Communication
They carry telephone signals, coax cables, and optical fibre to enable a global connection for voice, video, and the internet. More than 4.9 billion consumers worldwide depend on the wired internet daily.
3. Data Transfer
USB cables, HDMI cables, and Ethernet cables are used to connect computers, TVs, and other electronic devices into a larger network in which devices can share digital interactions. USB C can transmit data speedily at around 40 Gbps; thus, it is a highly efficient cable for connectivity on a global level.
How do Cables work?
Electricity, signals, or data travel through conductors, typically copper or fibre optic. The passage of information or energy from one point to another depends on the type of cable.
How Electricity and Data Travel through Cables
Copper cables
These are metal conductors (typically Copper or Aluminum) that are used for the transmission of electrical signals. When this cable carries the power an electric field will have developed around that wire as electricity travels through it. Copper cables will send signals of up to 10 Gbps over short runs, thus they are ideal for home networks and company connections.
Fiber Optic cables
Instead of using electricity, fibre optic cables transmit data via light signals. These cables are made up of thin glass or plastic fibres, which reflect and guide the light pulses from one end to the other. Compared to copper cables, fibre cables provide faster and more efficient communication optic cables are capable of transmitting data at speeds of 100 Gbps or more over long distances. This makes them the backbone of the Internet as well as international communications.
Difference Between Wired and Wireless Communication
The wired and wireless cables have different values in their way. Wired means stability and speed, while wireless networks endow an element of comfort and flexibility.
Pros of Wired Communication
Here are the advantages of wired communication:
- Much More Stable Connectivity: Wired networks sometimes do not have to rely on weather conditions or don’t cause any interference of signals, so they give us 24/7 access.
- Speedier Speeds: Up to 100 Gbps can be provided by the Ethernet or fibre optic cables with no effort. That’s why it is important for gaming, video streaming, and business use.
- Lesser Interference: It has wired signals, so there will not be any interruption-promise that is caused by walls, other devices, or radio waves.
Fact: 90% of global Internet traffic still goes through submarine fibre optic cables, which showcases that wired connections still form the backbone of the Internet.
Cons of Wired Communication
Here are the disadvantages of wired communication:
- Require Physical Setup: Setting up a wired network, including cables, consumes a lot of time and money.
- Limited Mobility: When you have to connect devices to the cable, it may restrict movement compared with wireless setups.
Pros of Wireless Communication
Here are the advantages of wireless communication:
- Much More Convenient & Flexible: Wireless networks enable the user to bring multiple gadgets together without cables.
- Easy Setting Up: With a Wi-Fi router, internet access can be made available to a whole home or office without nearly as much installation.
- Supports Mobile Device: Smartphones, laptops, and all forms of IoT devices rely on wireless technology to function.
Disadvantages of Wireless Communication
Here are the disadvantages of wireless communication:
- Signal Interference Occurs: Walls, microwaves, and other electronic devices will weaken your Wi-Fi signal and thus slow its speed.
- Security Risks: Wireless networks are not as secure from hackers as wired networks are secured. Therefore it require good encryption and safety measures.
Fact: According to estimates, damage from cybercrime is expected to cost $10.5 trillion globally per year by 2025. This amplifies the need for strong wireless security.
Importance of Cables in Daily Life
Cables are essential to modern life, they supply power to homes, offices, industries, and transportation. They form the backbone of electricity supply, internet connectivity, and communication networks to ensure smooth operations across almost every sector.
1. Powering Homes and Businesses
Using electrical cables allows your homes, offices, and industries to control electrical energy to power appliances, lighting, and machinery. Power grids are almost completely reliant on high-voltage transmission cables to transport electric power from stop to stop across towns and countries.
2. Internet and Telecommunication
The fiber optic and coaxial cables make sure high-speed internet is catered to customers and telecommunication services are reliable. Undersea submarine cables connect various countries across the globe for fast and stable broadband access.
Conclusion
Cables are the support of modern technology that gives power to homes, industries, and communication networks. They provide seamless connectivity by carrying electricity to the internet at infinite speeds.
Although wireless options are available, wired solutions are still far more reliable and secure. Given that the global cable market will probably exceed $250 billion by 2030, the role of cables in our daily lives will be enhanced further.